
The name Fishbone Diagram comes from the final shape of the diagram after analysing the problem because the structure looks like a fishbone, which is built gradually from right to left during the problem-solving session. – Service industry (5 Ss) : Surrounding, Suppliers, Systems, Skills, and Safety

– Marketing industry (7 Ps) : Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence
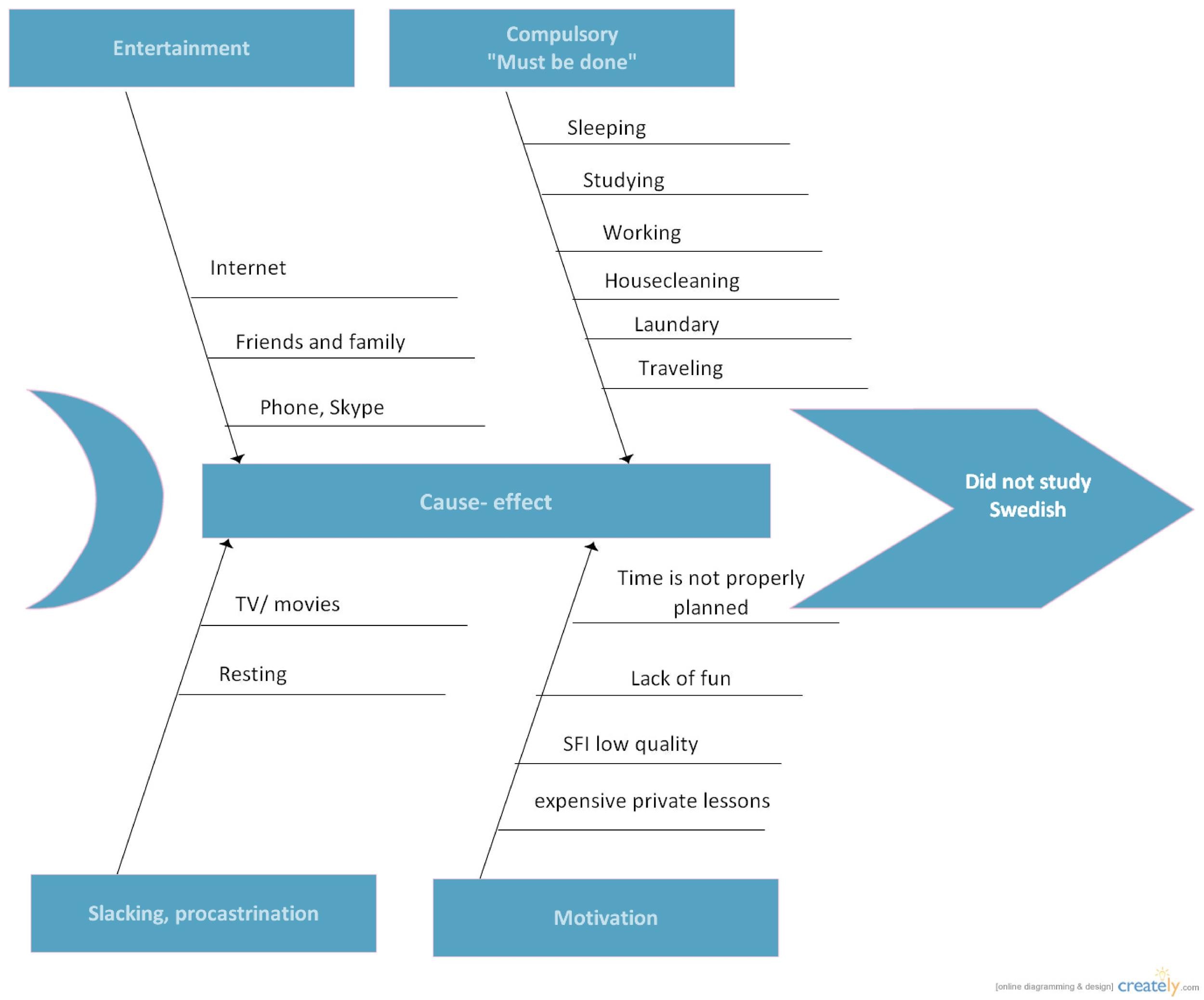
– Manufacturing industry (5 Ms) : Machine, Method, Material, Man Power, and Measurement The categorisation of the cause of a problem varies based on the industry, such as the following: The Cause and Effect Diagram can be implemented during the development brainstorming session to discover the roots of a specific problem or identify the bottleneck in a particular process by categorising the causes of problems into six main types: people, methods, machines, materials, measurements, and environment. The diagram is also known as the Ishikawa Diagram, Cause and Effect Diagram, and Herringbone Diagram. The term, Fishbone Diagram, was first coined by professor Kaoru Ishikawa in his book “Introduction to Quality Control,” published in 1990. Based on the results, the team can build an effective solution to eliminating the problem. The Fishbone diagram (also known as the root-cause analysis and Ishikawa diagram) is used to identify the root causes of problems by identifying the different factors that may cause the problem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
